 This month's T-SQL Tuesday is a week early due to the upcoming PASS Summit. It is being hosted by Stuart Ainsworth (blog | @codegumbo) and the topic is a general one: JOINs. I had an idea for a very brief post showing the typical join operations we use to solve common queries, and a more interesting but less common way we can solve the same queries with less code.
This month's T-SQL Tuesday is a week early due to the upcoming PASS Summit. It is being hosted by Stuart Ainsworth (blog | @codegumbo) and the topic is a general one: JOINs. I had an idea for a very brief post showing the typical join operations we use to solve common queries, and a more interesting but less common way we can solve the same queries with less code.
I often see people performing explicit outer or implicit anti semi joins to return "all of some set, except for this other set." Sometimes the query can get quite convoluted, leading to self-joins and CTEs – especially when aggregates are involved.
As a fictitious example, let's say we wanted all of the object_id values from sys.objects, except for those objects that also have a column named id – hey, I didn't say this was a real-world example, it's just a very simple way to demonstrate using objects I know you have installed. So you may see this type of explicit outer join:
SELECT o.[object_id] FROM sys.objects AS o LEFT OUTER JOIN sys.columns AS c ON o.[object_id] = c.[object_id] AND c.[name] = N'id' WHERE c.[object_id] IS NULL;
You may also see these NOT EXISTS or NOT IN variants:
-- NOT EXISTS: SELECT [object_id] FROM sys.objects AS o WHERE NOT EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM sys.columns WHERE [name] = N'id' AND [object_id] = o.[object_id] ); -- NOT IN: SELECT [object_id] FROM sys.objects WHERE [object_id] NOT IN ( SELECT [object_id] FROM sys.columns WHERE [name] = N'id' );
However, since SQL Server 2005, we've been able to use EXCEPT to write a slightly simpler version of this query:
SELECT [object_id] FROM sys.objects EXCEPT SELECT [object_id] FROM sys.columns WHERE [name] = N'id';
Sure, we've only saved a line or two, but I find the syntax much less complex – even on a trivial query like this. It doesn't look or smell like a join, does it? Well, it certainly behaves like one. In this case it also performs like one (though you should always test performance when weighing queries that produce the same results – readability should only be one of your criteria).
Let's generate the actual execution plans from within Plan Explorer. The runtime results are nearly identical for all four queries:
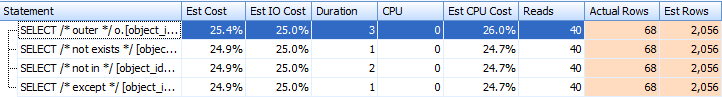
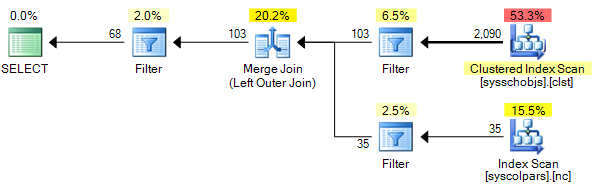
The graphical plans are almost identical. The outer join version looks like this:
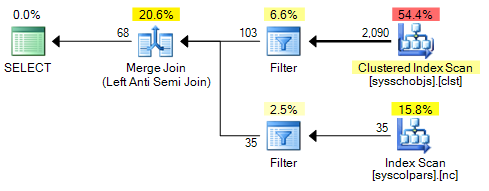
While the other three are all performed using one less filter, but otherwise the same plan:
In a future blog post, I'll go into more detail about EXCEPT and I'll also talk about how INTERSECT can make certain inner join queries more intuitive. These are definitely two operators that should be in your toolkit if you are writing a lot of joins…

